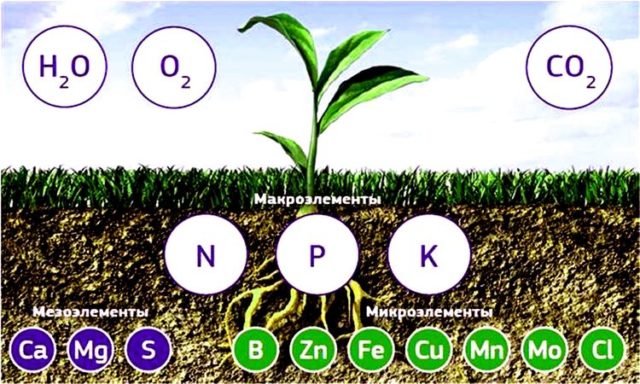
Without fertilizing, you will not grow crops even on fertile soils. Fertilizers containing basic and additional chemical elements are used in household and industrial fields. These are the food sources of plants. Different types of chelated fertilizers can be distinguished. They have an advantage over the usual ones, they increase the productivity of agriculture.
IMPORTANCE OF MICRO ELEMENTS IN PLANT LIFE
Nature has identified micronutrients for more than one function in plant life. They help in the most complete absorption of basic nutrients, water and solar energy. Microelements are part of enzymes that regulate the course of biochemical processes in plant cells. They increase the ability of tissues to regenerate, increase their resistance to negative environmental effects such as heat, cold, dry air and soil, excessive humidity, temperature changes and lack of lighting.
The lack of microelements leads to the weakening and poor condition of plants, retardation of development and flowering, deterioration of fruit. As a result, productivity decreases. The fruits are small, ugly and tasteless, their number decreases.
SIGNS OF MICRONUTRIENT DEFICIENCIES IN PLANTS
Although the amount of trace elements in plants is very small, their deficiency has a great impact on their vital activity. Iron is a part of enzymes, participates in the metabolism and synthesis of chlorophyll, oxidation and reduction reactions, and cellular respiration. Iron cannot pass from old tissues to young tissues, so its deficiency can be seen in the upper leaves: they become yellowish and whitish, the growth of shoots slows down.
Manganese participates in photosynthetic processes, synthesis of sugar and vitamins, activates enzymes necessary for nitrogen metabolism and other reactions, regulates water balance. Its deficiency is first detected in the upper leaves: yellowness appears between the veins, they themselves remain green. With a greater deficiency, spots appear on the leaves, growth slows down.
Copper regulates photosynthesis, is included in the composition of enzymes, increases the resistance of plants to fungal diseases, drought, heat and cold. Its deficiency is manifested by twisting and wilting of leaves, the appearance of chlorosis spots, darkening and dying of the edges of leaf plates. Plants are more susceptible to fungal diseases than ever before.
Molybdenum improves nutrition with calcium, participates in respiration and photosynthesis, nitrogen metabolism and enzyme synthesis. The disadvantage of this trace element is a red or orange border on the leaves, their deformation and death, the cessation of the growth of shoots. In molybdenum-deficient fruits, the concentration of nitrates increases, and the amount of vitamin C decreases.
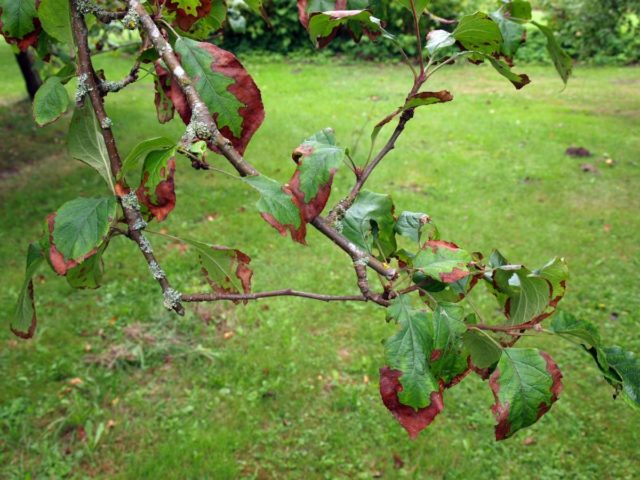

Zinc participates in the metabolism of proteins, carbohydrates and phosphorus, the synthesis of vitamins and auxins and affects the composition of fruits. The deficiency is manifested by the yellowing and discoloration of young leaves, their deformation and reduction, and the appearance of gray-brown and bronze spots scattered on the surface of the leaf. They turn brown and die. Stems become fibrous and thin, flowers stop growing and may fall. The root system rots.
Boron affects the development of tissues, especially young tissues (at growth points), regulates the number of phytohormones and activates vital processes in cells. Stimulates flowering, increases the number of fruits, makes plants resistant to diseases, including viruses. Its deficiency manifests itself in the peaks, burns appear on their faces, they bend over and die. The leaves become thin and brittle, necrotic tissue forms between the veins, and the stems acquire a reddish color. Seed ripening is disturbed.
FERTILIZERS WITH TRACE ELEMENTS IN CHELATED FORM
To normalize the content of trace elements in plant cells, it is necessary to constantly feed plants with complex fertilizers. It is recommended to use trace elements in the form of chelates. Chelates are a combination of a trace element and an organic substance in one molecule, in this form the elements are most fully absorbed.
Chelated fertilizers can be used for root irrigation and foliar spraying, pre-sowing seed treatment. You can mix them with regular fertilizers without micro-fertilizers, you can prepare solutions for drip irrigation.
TYPES OF CHELATED FERTILIZERS
Zinc, iron, copper, manganese, cobalt, boron, molybdenum are the main trace elements that are vital for plants with the participation of which chelated fertilizers are produced. Accordingly, there are zinc and copper chelates, etc. By the name of the chelate fertilizer, you can understand what elements are included in its composition.
Trace elements bind chelating components:
- EDTA (for soils with acidity pH 1.5-6).
- DTPA (acidity with pH 1.5-7).
- EDDNA (with acidic pH 3-10).
- EDP (acidity with pH 4.5-11).
Usually the type of chelating component is indicated on the packaging. One preparation can contain 1 trace element (monochelates) or several (complexes). They are available in powder (microcrystals) and liquid form.

PROS AND CONS OF THE APPLICATION
Chelates have undeniable advantages compared to micronutrient compounds in inorganic salts:
- dissolve well in water;
- easy to digest;
- do not change properties even in highly acidic soils;
- in this form, trace elements are protected from destabilization by other elements;
- it is perfectly absorbed by the roots and leaves of plants;
- non-toxic to plants and soil;
- washes out slower than soil;
- combined with pesticides and complex fertilizers (taking into account manufacturers’ recommendations).
The disadvantage of chelated fertilizers is the higher price than conventional fertilizers. The price also depends on the strength of the chelates themselves. Otherwise, they are in many ways superior to simple mixtures with trace elements.
WHAT PLANTS ARE CHELATES USED FOR?
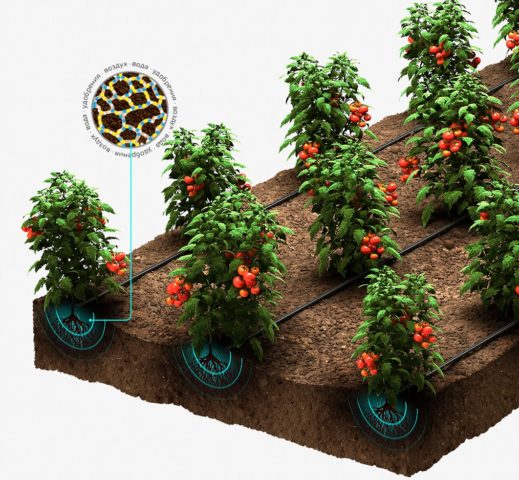
Solutions can be watered and sprayed on vegetables, fruits, berries, ornamentals, garden and indoor flowers (for example, chelated rose fertilizer is popular among rose growers for cutting, which improves the size and quality of the flower). There are no restrictions on their use, because all plants need trace elements for normal life.

Root irrigation is one way to apply chelated fertilizers
WHEN AND HOW TO APPLY CHELATE FERTILIZERS CORRECTLY
To achieve the best effect from chelates, they should be applied at certain periods of plant growth. For example, to process:
- seed before planting. Soaking in a fertilizer solution can be combined with a dressing, at the same time it is possible to disinfect the seeds and increase their germination.
- Seedlings and seedlings. After transplantation, watering with chelate solution accelerates the survival and development of plants in a new place, helps them to adapt faster, get used to non-standard environmental conditions and resist infections.
- Pre-flowering products that ensure reproduction and protection of the ovary.
- During fruit growth. Product and qualityt increases, it becomes sweeter, the tubers are starchy, they are stored longer, they show a decrease in the content of nitrates.
Chelates can be combined with pesticides, watered or sprayed on plants with solutions after chemical treatment. This allows plants to recover more quickly after application of agricultural chemicals.
WAYS TO USE CHELATED FERTILIZERS
Crystal and liquid chelate fertilizers can be used to prepare a solution. The seeds are soaked there, watered and sprayed under the root of the plant. At the same time, a significant efficiency of foliar nutrition is noted, as trace elements immediately enter the leaf tissues and are quickly completely absorbed by the plant.
Watering at the root has some disadvantages – with excessive moisture, part of the chelating elements will go to the soil, after which it will be unavailable to the crops. The problem can be solved by drip irrigation, which delivers water and its soluble substances to the roots of plants locally and in doses.
HOW TO MAKE DIY CHELATE FERTILIZERS
You can usually find liquid chelated fertilizers on sale. They are produced in this form because it is easy to use – you need to measure the required volume and dissolve it in water. Crystalline chelates should also be dissolved in water as indicated in the instructions.
You can prepare such fertilizers (copper and iron chelate) at home. You will need reagents: copper and iron sulfate, citric acid and pure distilled water.
The sequence of preparation of chelate fertilizers:
- Dissolve 8 g of iron sulfate in 2 liters of water.
- Dissolve 2 g of acid in another 5 liters of water.
- Slowly pour the first solution into the second, stirring the liquid continuously.
- Add another 1 liter of water to the resulting volume.
The output will be 5 liters of iron chelate fertilizer. It should be transparent, without turbidity and sediment, and have an orange color. It should be used immediately. Do not dilute, a new batch should be prepared if a larger volume is required.
Chelated copper fertilizer is prepared in the same way, but ascorbic acid (40 g) and copper sulfate (20 g) are taken.
Home-made chelated fertilizers are not stored and are less effective than industrial fertilizers, so it is recommended to use them for preventive application, not for quick treatment of plants from micronutrient deficiency.
CONCLUSION
From the experience of use on farms and individual households, chelated fertilizers are more effective than simple complexes with trace elements. They are easy to use, you don’t need to prepare complex solutions to feed vegetables or trees, you just need to dissolve the right amount of chelates in water. Although such fertilizers are expensive, the cost of their acquisition will pay off quickly after harvesting.